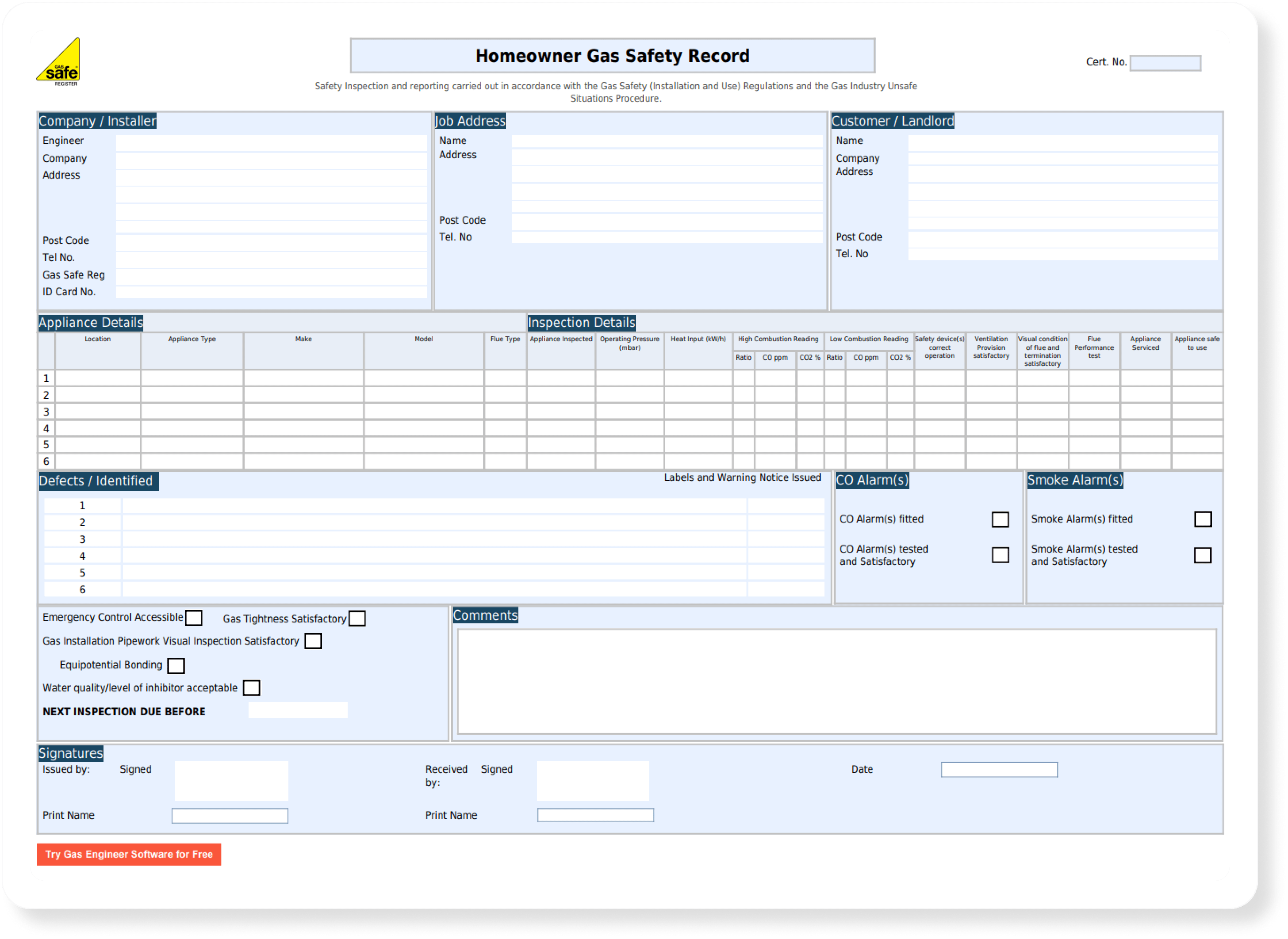
FREE TOOLS
Gas Pipe Sizing Calculator
Natural gas & LPG systems
Results:
You could be saving 6.6+ hours each week
From paperwork to managing customer details, Gas Engineer Software helps you get more out of your business.
How to use this gas pipe sizing calculator
Step 1: Enter a gross, net, or gas rate value. The other two will be automatically calculated for your reference.
Step 2: Enter the pipe length and all the fittings you plan on using for this section.*
Step 3: Some initial results will now appear on the right side. If the pressure drop displays red, the pipe diameter is too small. Adjust the pipe type until a green result appears. A green result indicates an acceptable pressure drop of less than 1 mbar for natural gas.
* For gas systems with multiple sections, you will need to add additional sections. Once you’ve added some information, the results will automatically update with separate and combined pressure loss figures.
Why use a gas pipe sizing calculator?
Save time & money
Our gas pipe sizing calculator will help you find the right size pipe far quicker than any manual calculation.
Get more done
The faster you know what you need to be doing, the quicker you get it done and move onto the next job.
Make fewer mistakes
Calculations done by hand are prone to human error. Get it right every time with a reliable
formula.
How to manually calculate pipe sizes for gas systems
In fact, our calculator is designed to use the exact same methodology stipulated by the British Standards BS 6891:2015 document fo gas pipe sizing.
The first thing you’ll need is access to some gas pipe size datasheets. Up-to-date tables for copper and steel pipes using natural gas and LPG can be found in the BS 6891:2015 document.
Step 1: Calculate the maximum gas rate of the appliance. To do this, you can multiply the maximum heat input (kW) by 0.095.
Step 2: Add up the total pipe length. This will include straight length of the pipe (m) and any fittings, which have the following equivalent lengths:
| Steel | Copper | 45° Bend | 90° Bend | 90° Elbow | Tee (Entering) | Tee (Exiting) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤1/2 inch | ≤15mm | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.40 | 0.75 | 1.20 |
| 3/4 inch | 22mm | 0.20 | 0.30 | 0.60 | 1.20 | 1.80 |
| 1 inch | 28mm | 0.25 | 0.40 | 0.80 | 1.50 | 2.30 |
| 1 1/4 inch | 35mm | 0.30 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 3.00 |
Step 3: Add up a total equivalent pipe length
Step 4: Cross-reference table A.1 or A.2 in BS 6891:2015 and guesstimate for an appropriate pipe size and it’s corresponding pressure loss per meter figure.
Step 5: Multiply the pressure loss per meter number by your total equivalent length (m) for a total pressure loss.
Step 6: If the total pressure loss is greater than 1mbar, repeat the process with a larger pipe diameter.
Make your job easier with
Gas Engineer Software
Efficient quoting, scheduling & certificates. All in one place.
Gas Engineer Software helps you manage your heating & plumbing business and save hours each week on admin and paperwork.